| DNA, the molecules of life | | The cell living Billions of years after the Big Bang, the energy that resulted in the phenomenon of inflation, after being gradually transformed into atoms and molecules, has given rise to molecular aggregates that currently allow life on our planet. These molecular aggregates and 'pop a complex molecule, DNA. This molecule has led to the construction of the living cell, a complex laboratory microscope, able to convert inorganic matter into useful energy for the operation of organic structures. The aggregation of organic cells led to the development of multicellular structures has therefore given rise to various types of agents in the macroscopic creatures today of our planet. Through a biological evolution lasted for millions of years and 'come to the current situation where there are life forms known to us. A process that can 'have occurred in every corner of the universe, wherever there are suitable conditions for its manifestation.
On our planet, the body of human beings and 'made up of about 60 trillion cells.
| 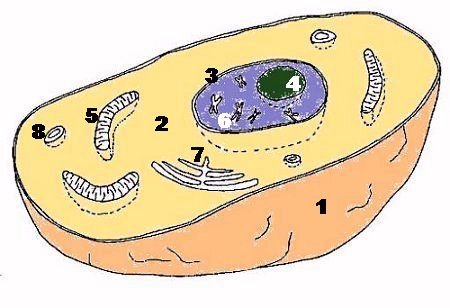 organic animal cell diagram organic animal cell diagram
[1] The cell membrane [2] The cytoplasm
[3] The core
[4] The nucleolus
| [5] Mitochondria [6] The chromosomes
[7] The Golgi apparatus
[8] Lysosomes
| | chromosomes Each cell has a nucleus within which contains the chromosomes. In humans, the nucleus contains 46 chromosomes that make up the gene pool of each individual. Chromosomes are rod-shaped organs (with order size tens of micrometers) in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and are visible only during cell division. During the resting phase of the cell material that makes up chromosomes and 'much less condensed form in the cell nucleus and a reticular pattern staining (chromatin). In relation to the functions of the nucleus, there are two types of living organisms:
a) = eukaryotic animal or vegetable organisms whose cells have a distinct nucleus from the cytoplasm - ie protozoa, plants and animals).
b) = prokaryotic organisms in which genetic material and 'immersed in the cytoplasm - ie blue-green algae, bacteria)
The chromosomes are defined with this name for their staining '. At first he was referring only to the organelles in the cell nucleus. Today is also extended to prokaryotes (where the chromosomes are composed of a circular molecule of DNA associated with proteins).
The chromosomes are composed of a single long thread-like molecule supercoiled and condensed with the creation of nucleic complex with a protein matrix that includes histones and other nucleoproteins.
In higher organisms the number and shape of chromosomes (the chromosomes) are specific and constant for each species. In
human somatic cell has 46 chromosomes, 22 pairs of chromosomes (called autosomes) and a pair of sex chromosomes (called eterocromosomi).
Chromosomes This pair can be equal (in females XX) or different (males: XY).
| 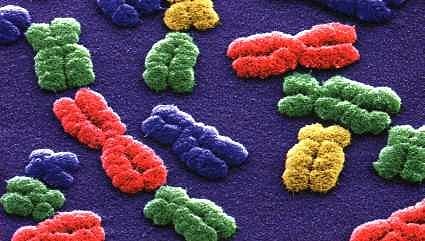 chromosomes chromosomes
| The helix of DNA Each chromosome and 'consists of a long strand of DNA molecule is compact on itself up to create the shape of each chromosome. DNA (or DNA) and 'acronym for deoxyribonucleic acid, a molecule responsible for the transmission and expression of hereditary characters. The total length of all filaments of the 24 human chromosomes reach the length of 2 meters. The thickness of this filament and 'ultramillesimale than a human hair. the electron microscope, the filament of the long DNA molecule turns out to be composed of two strands Twisted on themselves, forming the characteristic structure of the double helix, the helix of DNA
Each strand corresponds to a chain of nucleotides, formed each from:
a) a molecule of phosphoric acid
b) a sugar
c) a nitrogenous base
between the two long strands are placed four molecules, four bases (or nucleotides) chemicals: adenine (A), thymine ( T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G).
These nitrogenous bases are linked together and uniting the two strands, is displayed according to a fixed correspondence:
a) adenine with thymine
b) cytosine with guanine.
| 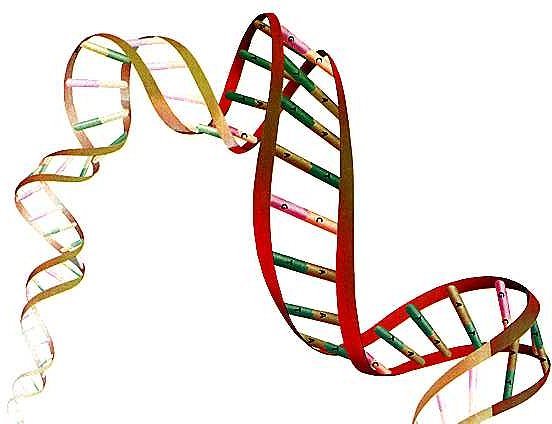 The double helix of DNA The double helix of DNA
| The genome small fraction of the long DNA molecule are areas that represent genes. The rest of the DNA seems to have no special duties if not the glue of the helical molecular structure that geneticists call "junk DNA" or junk DNA, 'cause it does not encode any protein. The gene is a unit 'of genetic material, consisting of small DNA segment, which contains the information for the synthesis of a single protein. The arrangement of four nitrogen molecules along the helix of DNA, the molecular area of \u200b\u200bthe gene, determines the genetic code of the individual. The sequence of the four nitrogenous bases located along the path of the two strands contains the genetic information (genetic code). The combined sequence of the arrangement of nitrogen bases is the pages of a book about his true ee which 'wrote the biological behavior of the individual.
It 's like the alphabet which is written an encyclopedia was made up of just four letters. In our case the linear sequence of these four letters, in different combinations, comprises all of our genetic heritage.
Of these letters the human genome contains about 3 billion and 300 million. Between a human and another succession of these letters is very similar but not identical, there is a difference of one letter per thousand (as, for example, the difference between a man and a chimpanzee is a hundred to a letter) . It is in these differences is that the diversity among individuals.
An encyclopedia is not 'made up only by a succession of letters, but' also consists of a series of volumes, which in this case can be compared to the chromosomes. In this perspective, the genome is an encyclopedia in 46 volumes, 23 and 23 coming from the father by her mother. The two groups
chromosomes are very similar because they have the same number of chapters. And the letters are very similar, but with small differences, namely the differences that exist between the father and mother. We are a bit 'a combination of these differences.
In each volume of this encyclopedia is also a number of chapters, namely that in every chromosome there are a number of different genes. Some will contain several chromosomes, others very few. The length of chapters varies: from just a thousand letters, ie the four chemical bases, up to several million.
The particular sequence of polynucleotides that forms the gene contains the information for the synthesis of the corresponding protein, usually one for each gene.
Not all genes are equally important. Some of them are essential for life, while others are redundant.
Since the '70s and 'can change the DNA sequence. The technique of recombinant DNA and 'a technique of genetic engineering that allows for molecules consisting of fragments from different organisms (to produce hormones, vaccines, etc.)..
Dictionary Genome GENOME: The entire genetic material of a cell. The set of genes of a creature. sequence a GENOME: DNA bases found so 'as they are willing in forming all the genes in a sample of a given species. COMPLETE THE GENOME: putting the foundations in the order in which genes are arranged on chromosomes. WRITE THE GENOME: find the functions of genes, or identify the characteristics of the protein controlled by them and the measures they are taking on the cells.
| 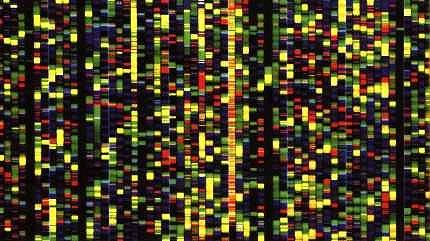 The genetic code of DNA seen in the computer The genetic code of DNA seen in the computer
| The RNA molecule DNA and 'assisted in his task management cell, the RNA molecule, an acronym acid ribonucleic acid. The RNA and 'a molecule polymer (polymers are organic compounds derived from the combination of two or more' simple molecules such monomori) very similar to DNA. The RNA is usually found in a single chain. were identified three types of RNA: a) messenger RNA (mRNA). Transferring genetic information from DNA to proteins that are synthesized in the ribosomes found in the cytoplasm of cells. b) ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Together with some protein and 'an essential constituent of ribosome (the DNA and' content in the nucleoli of the cell).
c) the transfer RNA (tRNA). are very small molecules about 80 nucleotides in length that act as interpreters between the nascent mRNA and protein with a specific code base that recognizes the two amino acids.
The genes responsible for the formation of ribosomal RNA is contained in the nucleoli, which correspond to certain regions of chromosomes, not separate from the core and which have no membrane separation from it.
| | Protein Proteins are the performers and the support of the combined work of the molecules of DNA and RNA. Proteins are organic substances containing nitrogen, high molecular weight and very complex structure, present in all forms of life (Animals, plants and microorganisms). Proteins are made up of long linear chains, called polypeptide chains of residues of alpha-amino acids (L-shaped). The amino acid sequence of a protein and 'a feature under the control of gene (protein synthesis = the set of events and reactions responsible for the biosynthesis of proteins).
proteins are particularly abundant in animals where plastics play functions and support (tasks that are assigned to the plant polysaccharides and especially cellulose).
In the body mass of the protein represents 15% by weight, most is found in muscle.
| |
 organic animal cell diagram
organic animal cell diagram  chromosomes
chromosomes  The double helix of DNA
The double helix of DNA  The genetic code of DNA seen in the computer
The genetic code of DNA seen in the computer  organic animal cell diagram
organic animal cell diagram  chromosomes
chromosomes  The double helix of DNA
The double helix of DNA  The genetic code of DNA seen in the computer
The genetic code of DNA seen in the computer
0 comments:
Post a Comment